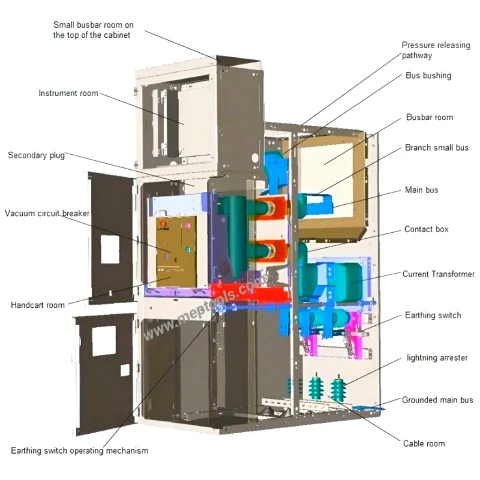
An explanation for medium voltage switchgear components :
1. Small Busbar Room (Top of the Cabinet): Houses busbars that distribute electrical power to different sections.
2. Pressure Releasing Pathway: Provides a controlled path to release pressure in case of an arc fault, ensuring safety.
3. Bus Bushing: Insulated components that allow the connection between different busbar sections.
4. Busbar Room: Contains the main busbars that distribute power to different outgoing circuits.
5. Branch Small Bus: Subdivides the power from the main bus to smaller branches.
6. Main Bus: The primary conductor for distributing electrical power within the switchgear.
7. Contact Box: Facilitates connections and ensures proper contact between different parts of the system.
8. Instrument Room: Houses measuring devices like voltage and current transformers for monitoring and protection.
9. Secondary Plug: Provides a connection point for auxiliary circuits and control wiring.
10. Vacuum Circuit Breaker (VCB): The main protective device that interrupts fault currents using a vacuum as the arc extinction medium.
11. Handcart Room: Allows for the insertion or withdrawal of the circuit breaker for maintenance or operational purposes.
12. Current Transformer (CT): Measures the current and provides input to protection and metering equipment.
13. Earthing Switch: Grounds the system during maintenance to ensure safety.
14. Lightning Arrester: Protects the switchgear from overvoltages caused by lightning or switching surges.
15. Grounded Main Bus: Connects the busbar to the ground for safety.
16. Cable Room: Houses power cables for incoming and outgoing circuits.
Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the switchgear, which is a key part of electrical distribution systems.
Reference Wikipedia: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Switchgear
#elec #engineering #switch_gear #medium_voltage






![FREE Irrigation autocad blocks download [DWG] | MEP Tools](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiV-RdjuRHRfloSECetjct_jqOzVmfLzlsj4cD1PO1I24x5bgvkHljsqtbzRMVt3ZEEp_3obsS2JfAtW9s3PpKRFdM84uFpb9giOFjFnB0Swn1it4Un9HJrzme5f1KH2Kczfe7KHb-nU01Iob8kFKT8xLo3qyPsiPl8exQBh7BnqPRZksvoXsb_tVJj85Y/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/FREE%20Irrigation%20autocad%20blocks%20download.jpg)



0 Comments